SpringBoot基础之Spring Boot快速入门
简介
在您第1次接触和学习Spring框架的时候,是否因为其繁杂的配置而退却了?在你第n次使用Spring框架的时候,是否觉得一堆反复黏贴的配置有一些厌烦?那么您就不妨来试试使用Spring Boot来让你更易上手,更简单快捷地构建Spring应用!
Spring Boot让我们的Spring应用变的更轻量化。比如:你可以仅仅依靠一个Java类来运行一个Spring引用。你也可以打包你的应用为jar并通过使用java -jar来运行你的Spring Web应用。
Spring Boot的主要优点:
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
快速入门
本章主要目标完成Spring Boot基础项目的构建,并且实现一个简单的Http请求处理,通过这个例子对Spring Boot有一个初步的了解,并体验其结构简单、开发快速的特性。
系统要求:
- Java 7及以上
- Spring Framework 4.1.5及以上
本文采用Java 1.8.0_73、Spring Boot 1.3.2调试通过。
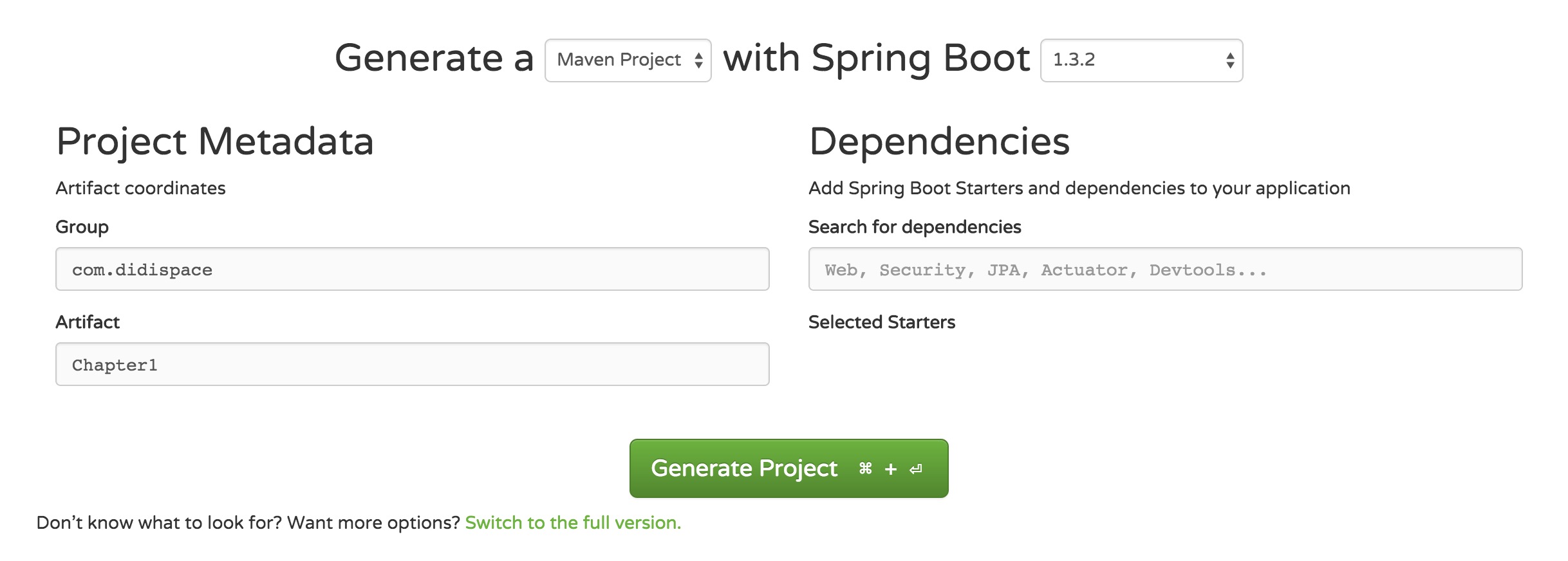
使用Maven构建项目
- 通过
SPRING INITIALIZR工具产生基础项目 - 解压项目包,并用IDE以
Maven项目导入,以IntelliJ IDEA 14为例:- 菜单中选择
File–>New–>Project from Existing Sources... - 选择解压后的项目文件夹,点击
OK - 点击
Import project from external model并选择Maven,点击Next到底为止。 - 若你的环境有多个版本的JDK,注意到选择
Java SDK的时候请选择Java 7以上的版本
- 菜单中选择
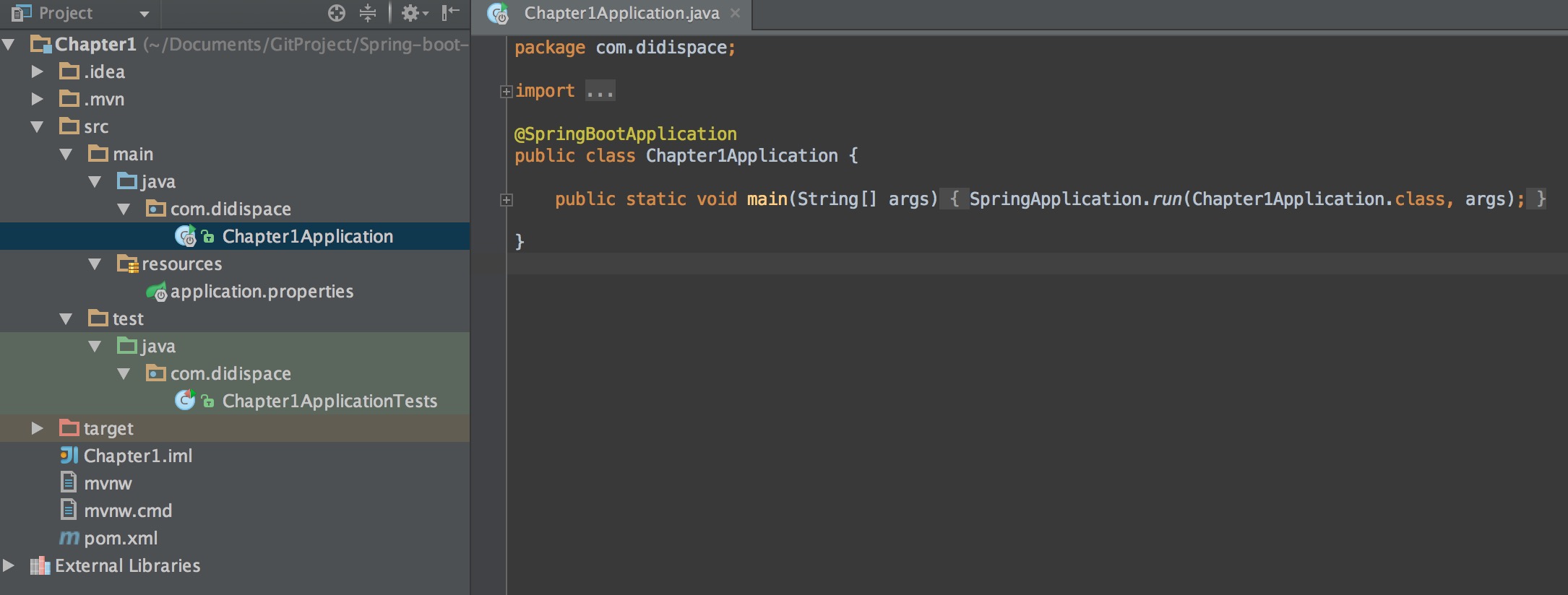
项目结构解析
通过上面步骤完成了基础项目的创建,如上图所示,Spring Boot的基础结构共三个文件(具体路径根据用户生成项目时填写的Group所有差异):
src/main/java下的程序入口:Chapter1Applicationsrc/main/resources下的配置文件:application.propertiessrc/test/下的测试入口:Chapter1ApplicationTests
生成的Chapter1Application和Chapter1ApplicationTests类都可以直接运行来启动当前创建的项目,由于目前该项目未配合任何数据访问或Web模块,程序会在加载完Spring之后结束运行。
引入Web模块
当前的pom.xml内容如下,仅引入了两个模块:
spring-boot-starter:核心模块,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAMLspring-boot-starter-test:测试模块,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>引入Web模块,需添加spring-boot-starter-web模块:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>编写HelloWorld服务
- 创建
package命名为com.didispace.web(根据实际情况修改) - 创建
HelloController类,内容如下
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String index() {
return "Hello World";
}
}- 启动主程序,打开浏览器访问
http://localhost:8080/hello,可以看到页面输出Hello World
编写单元测试用例
打开的src/test/下的测试入口Chapter1ApplicationTests类。下面编写一个简单的单元测试来模拟http请求,具体如下:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = MockServletContext.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
public class Chapter1ApplicationTests {
private MockMvc mvc;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
mvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new HelloController()).build();
}
@Test
public void getHello() throws Exception {
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/hello").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(equalTo("Hello World")));
}
}使用MockServletContext来构建一个空的WebApplicationContext,这样我们创建的HelloController就可以在@Before函数中创建并传递到MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup()函数中。
- 注意引入下面内容,让
status、content、equalTo函数可用
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;至此已完成目标,通过Maven构建了一个空白Spring Boot项目,再通过引入web模块实现了一个简单的请求处理。
本文转载自: http://blog.didispace.com/spring-boot-learning-1/
- 本文标签: Java Spring Boot
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。